The Ultimate Guide to Insulation Costs
Proper insulation is one of the most cost-effective ways to improve your home’s energy efficiency and comfort. With insulation costs ranging from $1.00 to $4.50 per square foot installed, understanding the factors that influence pricing helps homeowners make informed decisions about this valuable investment.
Cost Overview
The average cost to insulate a house ranges from $1,600 to $8,000, with most homeowners paying around $1,855 for a typical project. Costs vary significantly based on insulation type, area size, and installation complexity.
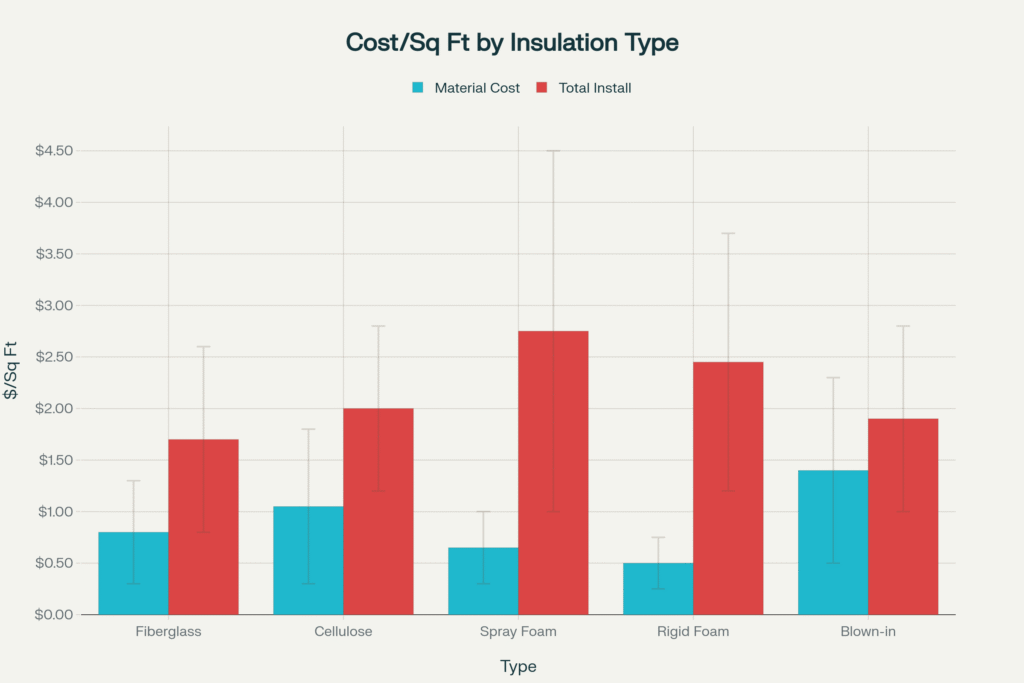
Insulation Cost Comparison: Material vs. Total Installed Costs Per Square Foot
Insulation Types and Costs
Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass remains the most budget-friendly option, with material costs ranging from $0.30 to $1.30 per square foot and total installed costs of $0.80 to $2.60 per square foot. This traditional insulation offers an R-value of 2.2 to 2.9 per inch and works well for walls, attics, and floors.
Advantages:
- Most affordable option
- DIY-friendly installation
- Resistant to moisture and mold
- Fire-resistant properties
Disadvantages:
- May settle over time
- Can leave gaps if improperly installed
- Lower R-value compared to premium options
Cellulose Insulation
Made from recycled materials, cellulose costs $0.30 to $1.80 per square foot for materials, with installed costs ranging $1.20 to $2.80 per square foot. It provides an R-value of 3.1 to 3.8 per inch, making it more efficient than fiberglass.
Benefits:
- Eco-friendly recycled content
- Higher R-value than fiberglass
- Excellent soundproofing properties
- Effective air sealing capabilities
Considerations:
- Requires professional installation equipment
- Can settle over time
- May retain moisture in humid conditions
Spray Foam Insulation
The premium option, spray foam insulation costs $1.00 to $4.50 per square foot installed. Two types are available:
Open-Cell Spray Foam:
- $0.44 to $0.80 per board foot
- R-value of 3.5 to 3.7 per inch
- Softer and more flexible
- Better for interior applications
Closed-Cell Spray Foam:
- $1.00 to $1.50 per board foot
- R-value of 5.0 to 7.0 per inch
- Superior moisture resistance
- Ideal for basements and crawl spaces
Rigid Foam Insulation
Rigid foam boards cost $0.25 to $0.75 per board foot for materials, with installed costs of $1.20 to $3.70 per square foot. These lightweight boards offer excellent thermal performance and are easy to install.
Blown-In Insulation
Blown-in insulation costs $1.00 to $2.80 per square foot installed. This method works particularly well for attics and existing walls, with materials including:
- Fiberglass: $0.50 to $1.10 per square foot
- Cellulose: $0.60 to $1.80 per square foot
- Rockwool: $1.40 to $2.10 per square foot
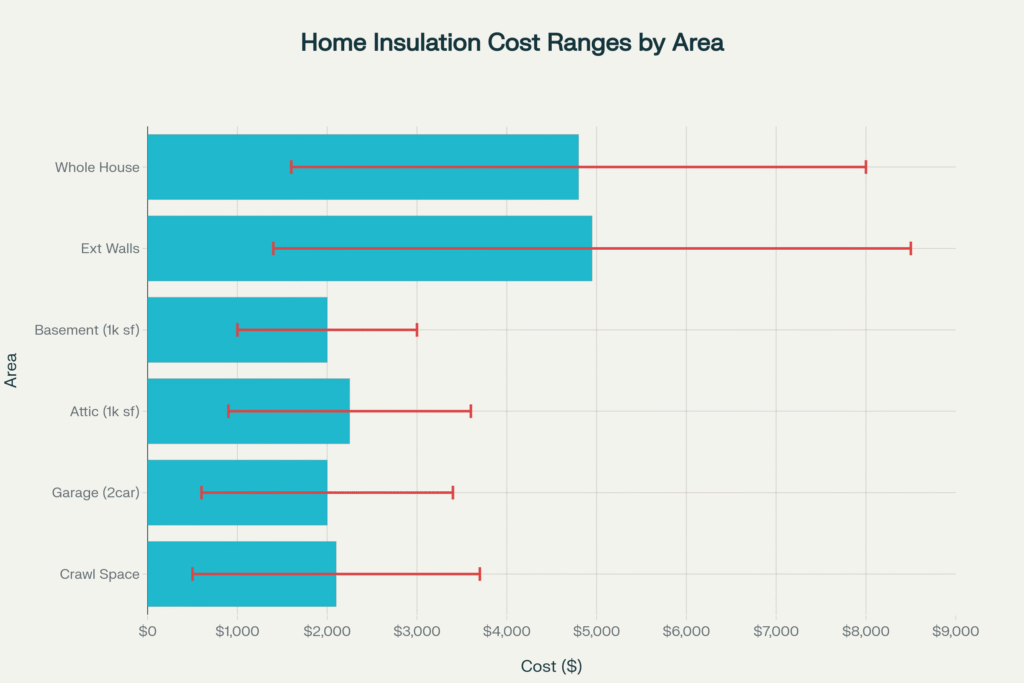
Home Insulation Costs by Area (2025)
Cost by Location
Attic Insulation
Attic insulation costs $1,500 to $6,000 for a typical project, or $1.50 to $2.45 per square foot. This is often the most important area to insulate, as rising heat creates significant energy loss through the roof.
Recommended R-Values:
- Cold climates: R-49 to R-60
- Moderate climates: R-38 to R-49
- Warm climates: R-30 to R-38
Wall Insulation
Wall insulation costs $1,400 to $8,500 for exterior walls throughout an entire house. The wide range reflects different installation methods:
- New construction: $0.80 to $2.60 per square foot
- Existing walls (injection foam): $1.60 to $4.20 per square foot
Basement Insulation
Basement insulation costs $1.50 to $2.50 per square foot on average, with total project costs ranging $1,400 to $6,300. Different areas require specific approaches:
- Basement walls: $4.29 to $6.29 per square foot
- Basement ceiling: $1.50 to $4.00 per square foot
- Rim joist: Included in comprehensive basement projects
Other Areas
- Crawl space: $500 to $3,700 total
- Garage: $600 to $3,400 total
- Mobile home: $700 to $5,000 total
Factors Affecting Costs
R-Value Requirements
Higher R-value insulation costs more but provides better thermal resistance. Climate zones determine minimum requirements:
- Zone 1-2 (South): R-30 to R-38 attic insulation
- Zone 3-4 (Moderate): R-38 to R-49 attic insulation
- Zone 5-8 (North): R-49 to R-60 attic insulation
Installation Complexity
Several factors increase installation costs:
- Accessibility: Hard-to-reach areas cost more to insulate
- Existing insulation removal: Adds $2 to $8 per square foot
- Air sealing requirements: May require additional services
- Custom fitting: Around pipes, ducts, and electrical work
Geographic Location
Labor costs vary significantly by region:
- High cost areas: $2.00 to $4.00 per square foot for labor
- Moderate cost areas: $1.00 to $2.50 per square foot for labor
- Lower cost areas: $0.50 to $1.50 per square foot for labor
Project Size
Larger projects often benefit from economies of scale:
- Small projects (under 500 sq ft): Higher per-square-foot costs
- Medium projects (500-1,500 sq ft): Standard pricing
- Large projects (over 1,500 sq ft): Potential bulk discounts
DIY vs. Professional Installation
DIY Costs
DIY insulation can save on labor costs but requires careful consideration:
Potential savings:
- Fiberglass batts: $0.30 to $1.30 per square foot (materials only)
- Blown-in: Requires equipment rental ($100-200 per day)
- Tools and safety equipment: $100 to $500 initial investment
DIY challenges:
- Safety concerns with insulation materials
- Risk of improper installation
- No warranty on workmanship
- Time-intensive process
Professional Installation Benefits
Professional installation costs more upfront but offers significant advantages:
- Expertise and proper technique
- Warranty coverage (typically 1-10 years)
- Proper safety protocols
- Access to premium materials
- Time efficiency
Cost comparison:
- DIY total costs: $0.50 to $1.50 per square foot
- Professional total costs: $1.50 to $4.50 per square foot
Return on Investment
Energy Savings
Proper insulation provides substantial energy savings:
- Average savings: 15% on heating and cooling costs
- Total energy savings: 11% on overall energy bills
- Cold climate homes: Up to 20% savings possible
Payback Period
Most insulation projects pay for themselves through energy savings:
- Typical payback: 3 to 7 years
- High-efficiency upgrades: 5 to 15 years
- Older homes: Often shorter payback periods
Home Value Increase
Insulation improvements add value to your property:
- ROI: Up to 117% return on investment
- Immediate value: Project cost typically recovered in home value
- Long-term benefits: Continued energy savings after payback
Cost-Saving Strategies
Timing Your Project
- Off-season installation: Contractors may offer discounts during slower periods
- Bundle projects: Combine insulation with other energy efficiency improvements
- Tax incentives: Federal and state rebates can offset costs
Prioritizing Areas
Focus on high-impact areas first:
- Attic insulation: Greatest energy savings potential
- Air sealing: Complement insulation with proper sealing
- Basement rim joist: Often overlooked but cost-effective
- Wall insulation: Consider for older homes with minimal insulation
Material Selection
Balance cost and performance:
- Budget option: Fiberglass batts for DIY projects
- Best value: Cellulose blown-in for professional installation
- Premium choice: Spray foam for maximum efficiency
Planning Your Insulation Project
Energy Audit
Consider a professional energy audit ($300-500) to identify:
- Current insulation levels
- Air leakage problems
- Priority improvement areas
- Potential energy savings
Getting Quotes
When obtaining contractor quotes:
- Get multiple estimates (3-5 contractors)
- Verify licensing and insurance
- Check references and reviews
- Compare materials and R-values
- Understand warranty terms
Permits and Codes
Most insulation projects don’t require permits, but check:
- Local building codes
- HOA requirements
- Utility rebate program requirements
Special Considerations
Climate-Specific Needs
Different climates require different approaches:
Hot climates:
- Focus on radiant barriers
- Consider reflective insulation
- Emphasize air conditioning load reduction
Cold climates:
- Higher R-value requirements
- Moisture management critical
- Consider vapor barriers
Mixed climates:
- Balanced approach needed
- Seasonal performance considerations
Health and Safety
Important safety considerations:
- Asbestos testing in homes built before 1980
- Proper ventilation during installation
- Mold prevention through moisture control
- Fire safety with proper materials selection
Investing in quality insulation provides immediate comfort improvements and long-term financial benefits. While initial costs may seem significant, the combination of energy savings, increased home value, and improved comfort makes insulation one of the most cost-effective home improvements available. Whether choosing budget-friendly fiberglass or premium spray foam, proper insulation installation pays dividends for years to come.

