The Ultimate Guide to Electrician Costs
Understanding electrician costs is essential for homeowners planning electrical projects, from simple outlet installations to complete home rewiring. This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about electrician pricing, factors that influence costs, and how to make informed decisions when hiring electrical professionals.
Standard Electrician Hourly Rates
Electrician hourly rates vary significantly based on experience level and specialization. The typical range is $50 to $130 per hour, with most electricians charging a service call fee of $100 to $200 that covers the first hour of work.

Average Hourly Rates by Electrician Type and Experience Level
The pricing structure typically includes several components beyond the basic hourly rate. Service call fees cover travel time and initial diagnostics, ensuring electricians are compensated for their time regardless of project duration. Many contractors use flat-rate pricing for common services, providing customers with predictable costs and eliminating hourly billing uncertainty.
Common Electrical Service Costs
Homeowners can expect varying costs depending on the type of electrical work needed. Small electrical projects typically range from $141 to $419, while larger projects can cost $2,000 to $6,000 or more.
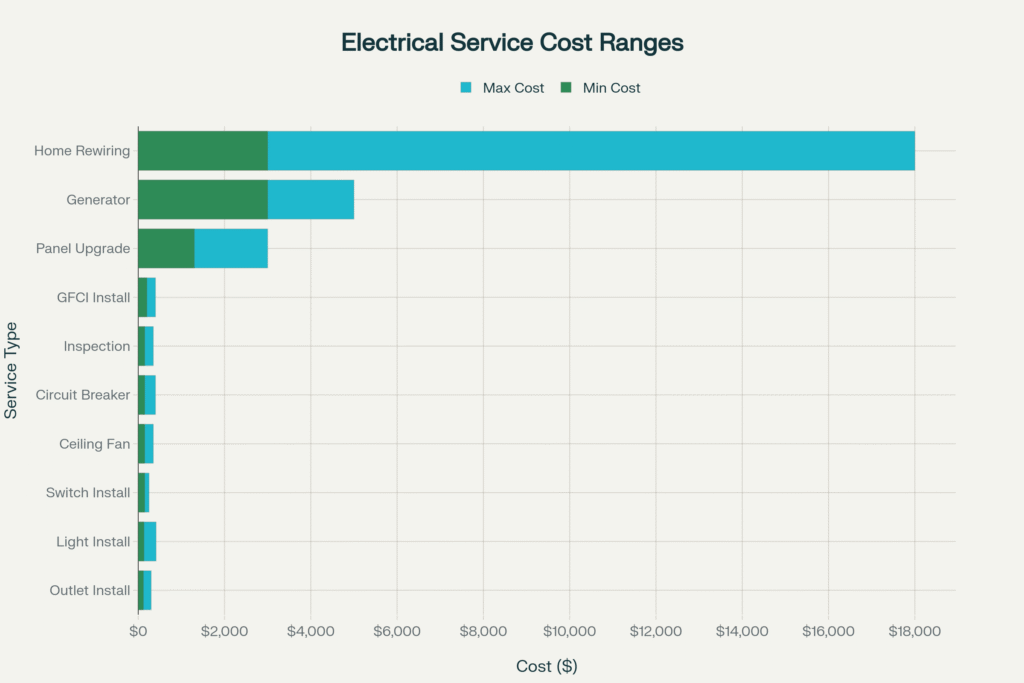
Common Electrical Services and Their Typical Cost Ranges
Detailed Service Breakdown
Basic Installations and Repairs
- Outlet installation or replacement ranges from $120 to $300, with GFCI outlets commanding higher prices due to safety features and installation complexity
- Light fixture installations typically cost $133 to $414, depending on fixture complexity and whether new wiring is required
- Electrical switch installations average $150 to $250 for standard replacements
Electrical Panel and Circuit Work
- Circuit breaker replacement costs $150 to $400, with specialty AFCI or GFCI breakers costing more but providing enhanced safety protection
- Electrical panel upgrades from 100 to 200 amps typically range from $1,300 to $3,000, representing one of the most significant residential electrical investments
Major Electrical Projects
- Complete home rewiring projects range from $3,000 to $18,000, depending on home size and complexity
- Generator installations cost $3,000 to $5,000 for whole-house systems
Factors That Influence Electrician Costs
Multiple factors significantly impact the final cost of electrical services, often creating substantial price variations for similar projects.
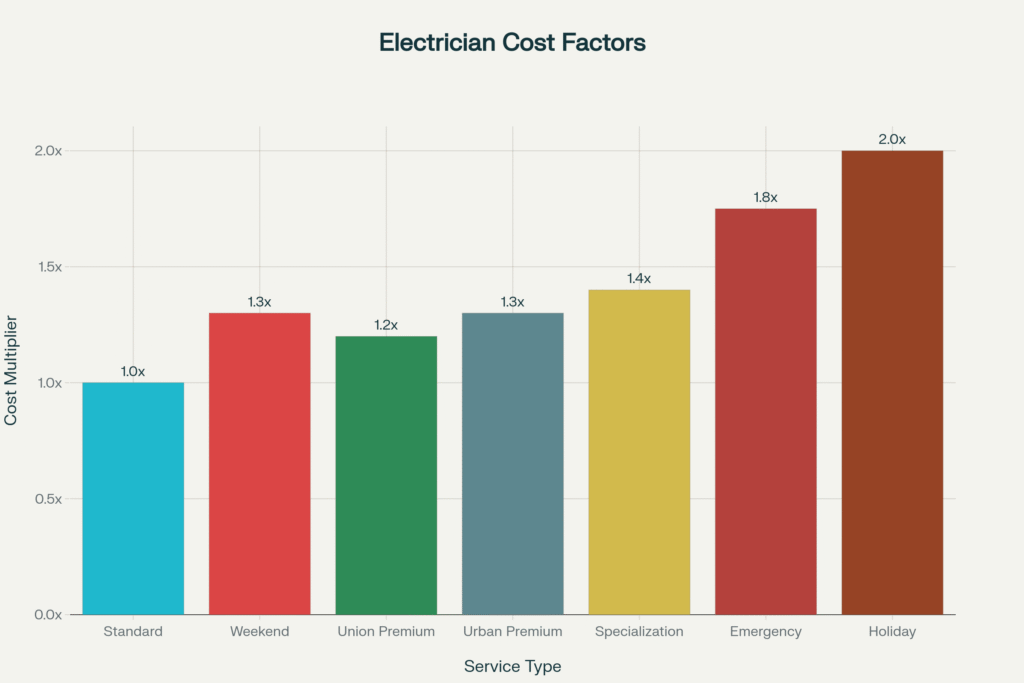
Cost Multipliers for Different Electrician Service Factors
Geographic Location and Regional Variations
Location plays a crucial role in determining electrician costs. Urban areas typically charge 30% more than rural locations due to higher operating costs, increased demand, and elevated cost of living. States with strong union presence and high living costs generally offer higher compensation, with electricians in California, New York, and Illinois earning significantly more than those in southern states.
Union vs. Non-Union Considerations
Union electricians typically earn 20% higher wages than their non-union counterparts, along with better benefits and job security. However, non-union electricians often offer more flexibility in scheduling and pricing, potentially providing cost savings for residential customers.
Experience and Specialization Premiums
Experience directly correlates with pricing power. Master electricians with specialized skills can command 40% higher rates than journeyman electricians. Specialists in high-demand areas like solar installations, smart home technology, or electric vehicle charging systems often charge premium rates due to specialized knowledge and limited competition.
Emergency and After-Hours Services
Emergency electrical services command significant premiums due to the urgent nature and disruption to normal schedules. Emergency rates typically range from $150 to $200 per hour, representing a 75% to 100% premium over standard rates. After-hours, weekend, and holiday services can cost double standard rates or more.
Understanding Electrician Business Economics
Professional electrical contractors operate complex businesses with substantial overhead costs and profit margin requirements that directly influence pricing.
Overhead and Operating Expenses
Electrical contractors typically factor overhead costs at 13-20% of total sales. These expenses include vehicle maintenance, insurance, licensing fees, tools, office expenses, and employee benefits. Quality contractors invest in proper insurance coverage, ongoing training, and professional equipment, costs that are reflected in their pricing structure.
Profit Margin Expectations
Successful electrical businesses target 10-20% net profit margins, with gross profit margins typically ranging from 65-67%. Contractors operating below these margins often compromise on service quality, safety, or business sustainability. Understanding these economics helps customers appreciate why extremely low bids may indicate corner-cutting or inexperienced providers.
When to Call an Electrician: Safety Considerations
Certain electrical situations require immediate professional attention to prevent safety hazards or property damage.
Emergency Situations
Call an emergency electrician immediately for smoking outlets, burning smells, frequent circuit breaker tripping, sparks or arcing, and power outages affecting only part of your home. These symptoms can indicate serious wiring problems that pose fire risks or electrocution hazards.
Routine Maintenance and Upgrades
Schedule professional electrical inspections for homes over 25 years old, when adding major appliances, or before buying/selling property. Electrical inspections typically cost $150 to $350 and can identify potential problems before they become emergencies.
DIY vs. Professional Work: Safety and Legal Considerations
While some minor electrical tasks might seem approachable for DIY enthusiasts, electrical work carries significant risks that often outweigh potential savings.
Risks of DIY Electrical Work
DIY electrical work increases fire risk, electrocution danger, and code violation penalties. Improper installations can void insurance coverage, create liability issues, and result in costly corrections when discovered during inspections. Electrical fires cause approximately 51,000 home fires annually, resulting in $1.3 billion in property damage.
Code Compliance and Permits
Professional electricians ensure work meets National Electrical Code requirements and local regulations. Electrical permit fees typically range from $50 to $200, depending on project scope and location. Code violations can result in fines reaching thousands of dollars, failed inspections, and reduced property values.
How to Choose the Right Electrician
Selecting a qualified electrical contractor requires careful evaluation of credentials, experience, and business practices.
Essential Qualifications
Verify active licensing, insurance coverage, and professional certifications before hiring any electrician. Licensed electricians have completed required training and passed competency examinations, ensuring they understand current electrical codes and safety practices.
Evaluation Criteria
Request multiple quotes to compare pricing and scope, but avoid automatically choosing the lowest bid. Extremely low quotes often indicate inexperienced contractors, substandard materials, or hidden costs that emerge later. Quality contractors provide detailed written estimates, clear timelines, and warranty information.
Communication and Professionalism
Professional electricians respond promptly to inquiries, explain work clearly, and provide written contracts. They should offer references from recent projects and demonstrate knowledge of local codes and regulations. Clear communication about project scope, potential challenges, and pricing helps establish realistic expectations.
Cost-Saving Strategies
Homeowners can manage electrical costs while maintaining safety and quality standards through strategic planning and informed decision-making.
Project Planning and Timing
Bundle multiple electrical projects to reduce service call fees and leverage economies of scale. Plan non-emergency work during standard business hours to avoid premium pricing. Standard weekday service costs 30-75% less than emergency or weekend rates.
Material Considerations
High-quality electrical materials cost more initially but provide better long-term value through improved safety, reliability, and code compliance. Discuss material options with your electrician, understanding that cheaper components may require more frequent replacement or create safety risks.
Long-term Investment Perspective
Electrical upgrades often provide return on investment through improved safety, increased home value, and energy efficiency. Panel upgrades, GFCI installations, and modern wiring systems reduce long-term maintenance costs and insurance risks while supporting modern electrical demands.
Conclusion
Electrician costs reflect the complexity, risk, and expertise required for safe electrical work. While prices vary significantly based on location, project scope, and timing, investing in qualified professionals protects your safety and property value. Understanding these cost factors empowers homeowners to make informed decisions, budget appropriately, and prioritize electrical projects that offer the greatest safety and value benefits.
Remember that electrical work is not an area where cost-cutting typically pays off. Quality electrical contractors provide essential services that protect lives and property, making their expertise a worthwhile investment in your home’s safety and functionality.

